How to Navigate the Legal Process for Phone Rental Recovery (In 1 Read!) | 57% Success Rate in Recovering Overdue Payments
Core Summary
To help more leasing platforms and merchants understand the civil litigation process and enforcement procedures for mobile phone rental disputes, we have compiled the "Civil Litigation and Enforcement Guide" based on the latest laws and judicial interpretations.
This guide primarily covers:
Required documentation
Litigation procedures
Enforcement measures
Litigation serves as a critical tool to protect merchants' legitimate interests. According to industry data from XINZU, legal action can recover 32.8% to 57.3% of overdue rental payments.
Step 1: Pre-Filing Preparation
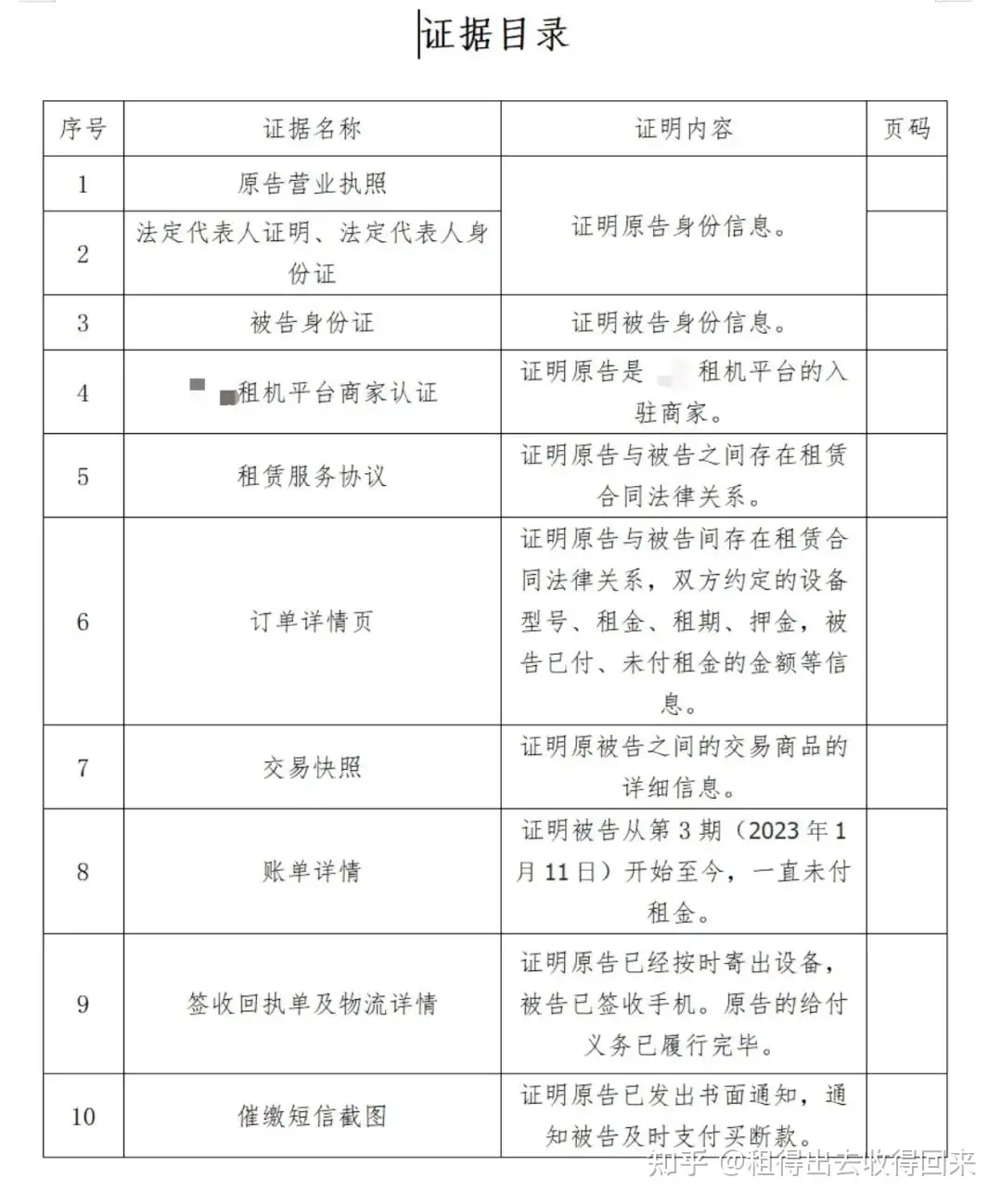
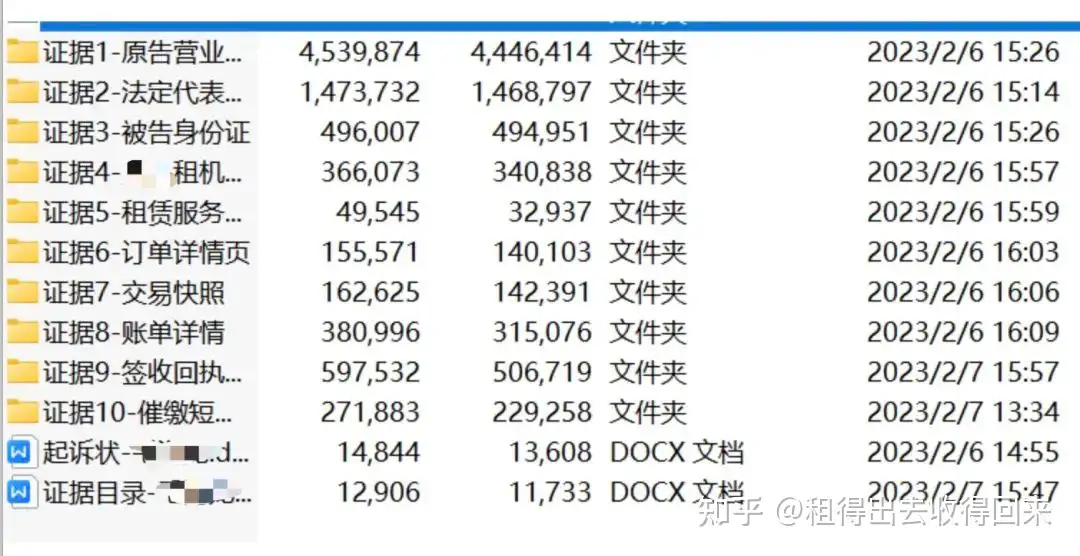
Evidence Collection and Documentation
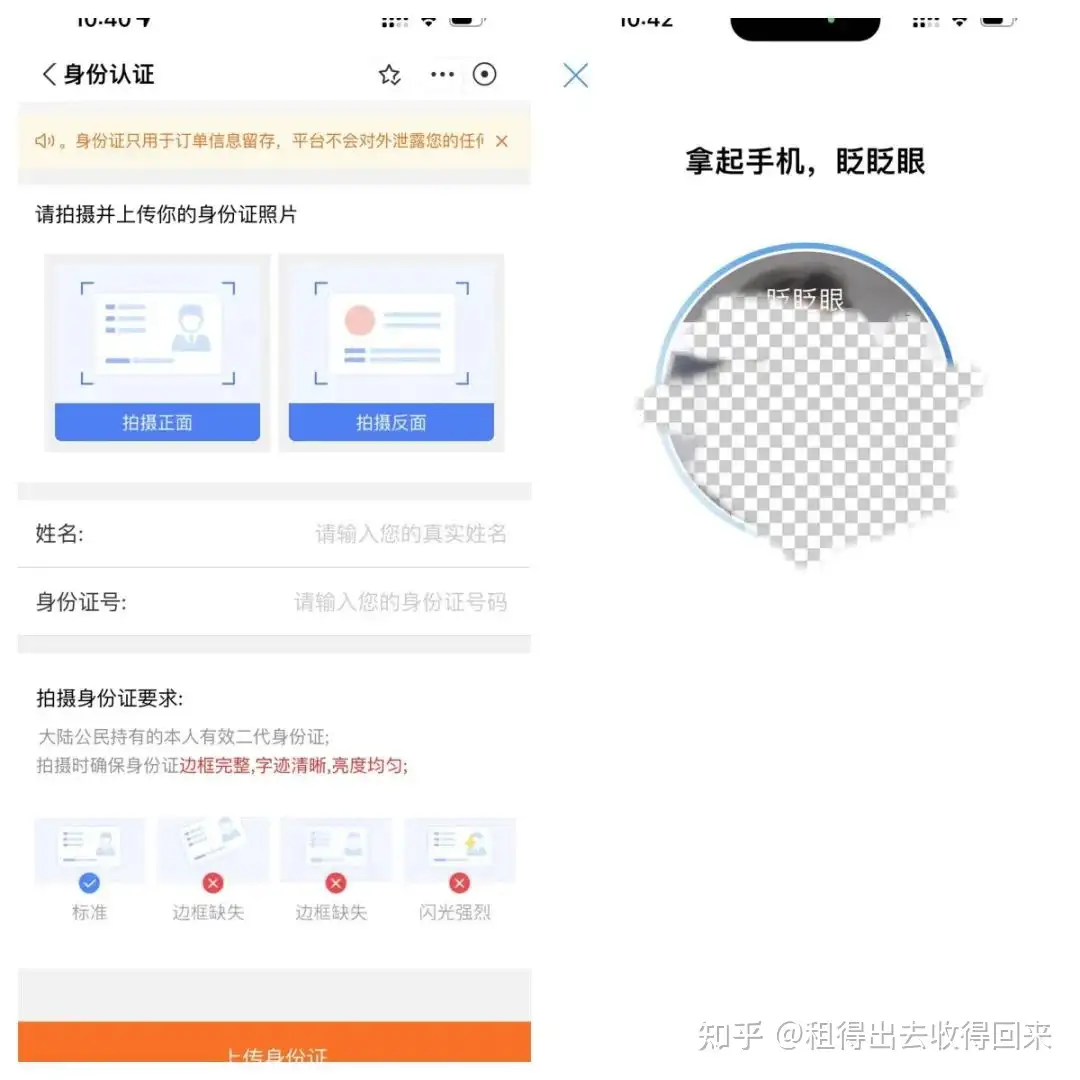
1. Identity Verification
User-uploaded ID card copies
Alipay facial recognition verification records
Proof of identity and confirmation of genuine application
2. Evidence Establishing Legal Relationships
Lease Service Agreement
Credit Inquiry Agreement
Digital Certificate Usage Agreement
Privacy Policy and other electronic evidence

Key Focus: The Lease Service Agreement
Based on analyses of mobile phone credit lease cases nationwide, merchants should pay attention to the following:
Contract Legality: Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations
Rent Payment & Overdue Handling: Clearly define payment deadlines, consequences of default, and conditions for converting lease-to-own
Advance Payments & Deposits: Specify refund conditions for deposits and prepaid rents
Written Notices: Maintain evidence of notifications (SMS, email, delivery receipts)
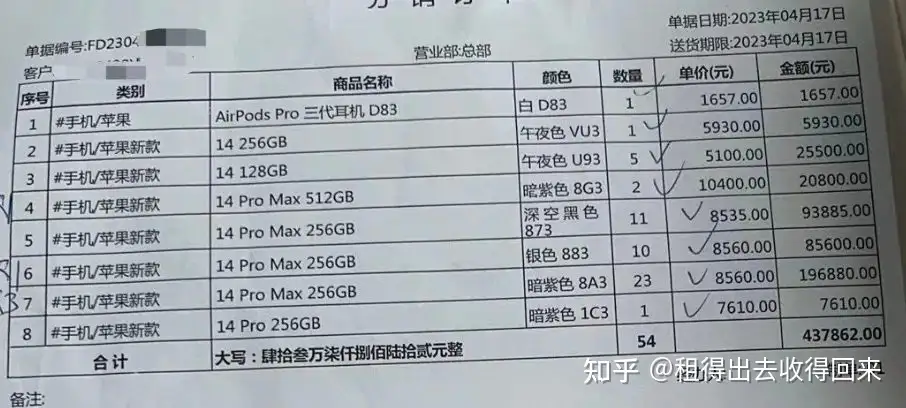
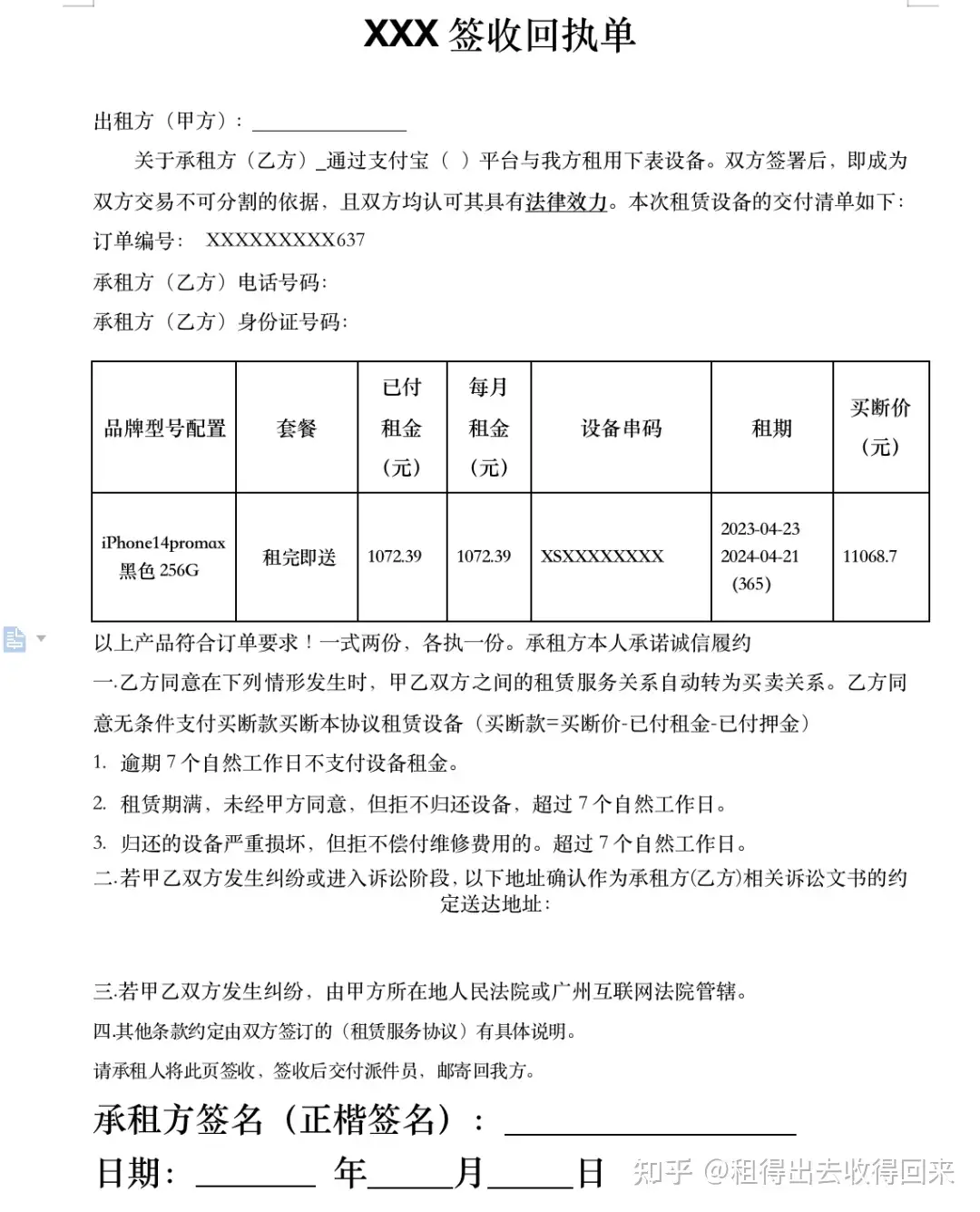
3. Supporting Evidence
Delivery receipts
Device procurement invoices
WeChat chat records
Signed acknowledgment receipts
Electronic or paper-based signature confirmations
Step 2: Drafting the Complaint
(Can be handled by legal counsel thereafter)
Submit the complaint to the court with copies for all defendants (Number of Defendants + 1)
Contents of the complaint:
Plaintiff's details
Defendant's information
Claims and objectives
Facts and reasoning
Evidence list
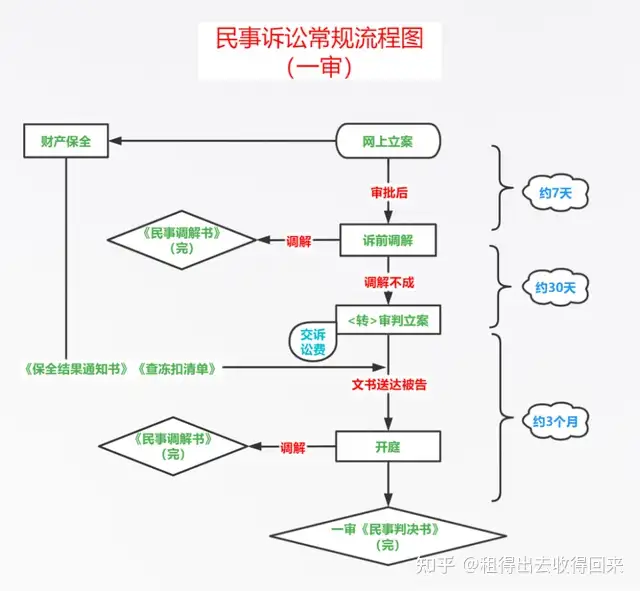
Step 3: Filing with the Competent Court
Jurisdiction typically lies where the defendant is located
Courts must accept cases that meet legal requirements within 7 days
Pay litigation fees within 7 days of acceptance
Submit property preservation applications if needed
Step 4: Service of Process
Courts typically attempt mediation first (30-day period)
If mediation fails, formal service occurs within 15 days to 2 months
Multiple delivery methods attempted before公告送达 (public notice service)
Step 5: Court Hearing Notification
Plaintiffs must attend or risk case dismissal
Defendants risk default judgment if absent
Court notices issued 3 days before hearing
Step 6: Court Proceedings
Identity Verification
Court Investigation
Plaintiff states claims and facts
Defendant responds
Evidence Examination
Both parties present and challenge evidence
Court Debate
Parties present arguments
Court Deliberation
Parties sign hearing records
Step 7: Judgment Issuance
Public announcement of verdict
15-day appeal period for judgments
10-day appeal period for rulings
Step 8: Enforcement
Application
Submit enforcement application and judgment documents
Execution
Follow up with enforcement judge within 15 days
Measures
Property seizure
Account freezing
Credit blacklisting
Restrictions
Ban on high-consumption activities
Travel restrictions
Luxury purchase prohibitions
Relevant Civil Code Provisions
Article 509: Good faith performance of contract obligations
Article 577: Liability for breach of contract
Article 585: Stipulated违约金 (breach penalties)
Articles 626/628: Payment amount, method, and timing requirements
Conclusion
When conducting mobile phone credit leasing business, merchants should focus on contract legality, clear rights and responsibilities, and strengthened credit risk control to ensure smooth operations and reduce dispute risks.
Source: Compiled based on latest judicial practices and industry data analysis.










